Voltage
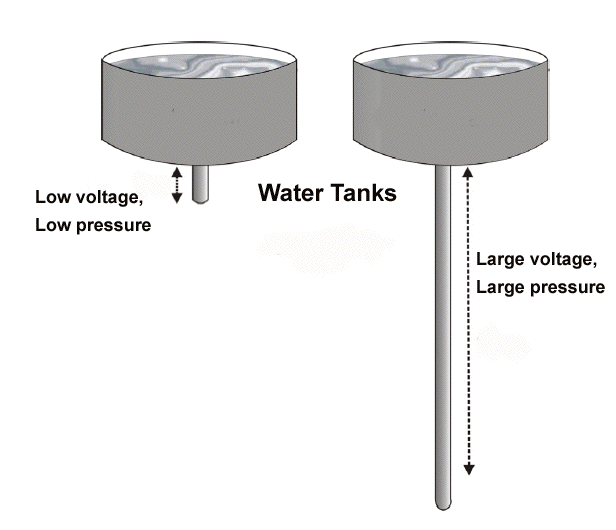
The pressure that pushes electrons in a wire is called voltage. Using the water pipe analogy, if a water tank was suspended a small distance above the ground with a short pipe coming out of the bottom, the water pressure would be similar to the force of a very weak, low pressure shower (left image below). If the same water tank were suspended above the ground with a longer pipe, the shower’s water pressure would be much larger, possibly enough to knock you down (right image below).
Voltage (V) is a measure of the pressure applied to electrons to make them move. It is a measure of the strength of the current in a circuit and is measured in volts (V). Just as the longer pipe applies greater pressure than the smaller pipe, a car battery (12 V) would apply greater pressure than a lower-voltage AA battery (1.5 V).
The standard voltage of wall outlets in the United States is 120 V. An electric clothes dryer is usually wired at 240 V.
