Download the Climate Change Unit Instructional Framework (PDF)
The framework document includes enduring understandings, essential questions, standards alignments, and an overview of the instruction and learning activities.
The Climate Change curriculum uses a spatial learning design model that incorporates a related set of frameworks and design principles to provide guidance in the development of the geospatial information technologies (GIT)-supported curriculum materials.
The framework includes:
- Align materials and assessments with learning goals.
- Contextualize the learning of key ideas in real-world problems.
- Engage students in scientific practices that foster the use of key ideas.
- Use geospatial technology as a tool for learners to explore and investigate problems.
- Support teachers in adopting and implementing GIT and inquiry-based activities.
The curriculum materials are designed to align instructional materials and assessments with learning goals. National and state standards are used to provide guidelines for important science content in addition to the science inquiry and spatial thinking skills that schools must focus on.
The materials use a series of proven design principles to promote spatial thinking skills with Earth and environmental science materials:
- Design curriculum materials to align with the demand of classroom contexts.
- Design activities to apply to diverse contexts.
- Use motivating contexts to engage learners.
- Provide personally relevant and meaningful examples.
- Promote spatial thinking skills with easy-to-use geospatial learning technologies.
- Design image representations that illustrate visual aspects of scientific knowledge.
- Develop curriculum materials to better accommodate the learning needs of diverse students.
- Scaffold students to explain their ideas.
A simplified visual that reflects the main curriculum activity structures are included on the top of each instructional sequence page:
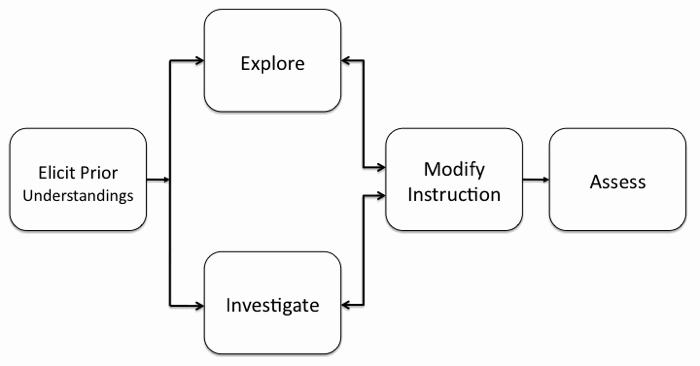
Elicit Prior Understandings.
At the beginning of the unit, the teacher evaluates what students know through a content knowledge pretest.
Explore and Investigate.
Students explore and investigate concepts through geospatial-supported investigations, laboratory experiments, and other curricular materials to help them acquire desired knowledge, skills, and attitudes.
Modify Instruction.
The teacher adjusts instruction as needed based on students' responses to the learning activities (formative assessment).
Assess.
At the end of the unit, the teacher evaluates students through their completed artifacts, embedded assessments, and a content knowledge posttest.
